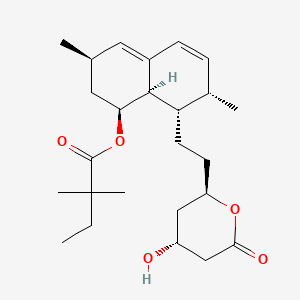
D0111 | Simvastatin
A
C
C10BX04 Simvastatin, acetylsalicylic acid and ramipril
[C10BX] HMG CoA reductase inhibitors, other combinations
[C10B] LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, COMBINATIONS
[C10] LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
[C] Cardiovascular system
C10BX01 Simvastatin and acetylsalicylic acid
[C10BX] HMG CoA reductase inhibitors, other combinations
[C10B] LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, COMBINATIONS
[C10] LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
[C] Cardiovascular system
C10BA04 Simvastatin and fenofibrate
[C10BA] HMG CoA reductase inhibitors in combination with other lipid modifying agents
[C10B] LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, COMBINATIONS
[C10] LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
[C] Cardiovascular system
C10BA02 Simvastatin and ezetimibe
[C10BA] HMG CoA reductase inhibitors in combination with other lipid modifying agents
[C10B] LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, COMBINATIONS
[C10] LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
[C] Cardiovascular system
C10AA01 Simvastatin
[C10AA] HMG CoA reductase inhibitors
[C10A] LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS, PLAIN
[C10] LIPID MODIFYING AGENTS
[C] Cardiovascular system
A10BH51 Sitagliptin and simvastatin
[A10BH] Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors
[A10B] BLOOD GLUCOSE LOWERING DRUGS, EXCL. INSULINS
[A10] DRUGS USED IN DIABETES
[A] Alimentary tract and metabolism
| Toxicity | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPENING OF PERMEABILITY TRANSITION PORE (PTP) | 10 µM | 1 hour | Human | HepG2 | High-content screening assay | Decrease | MEC | 306 |
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 76.5 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Rh123 fluorescence (excitation 485 nm, emission 535 nm) are recorded using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (mCICCP (20 µM) treatments was considered as the 100% baseline for ΔΨm loss) | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| MEMBRANE POTENTIAL | 50 µM | 1 hour | Human | HepG2 | High-content screening assay | Decrease | MEC | 306 |
| RESPIRATION | 1.6 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | decrease | EC20 | 36 |
| RESPIRATION | ND | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | Negative | EC20 | 36 |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex I activity | decrease | p < 0.01 | 3 | |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex II + III activity | decrease | p < 0.001 | 3 | |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex II + III activity | decrease | p < 0.001 | 3 | |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex IV activity | decrease | p < 0.001 | 3 | |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex V activity | decrease | p < 0.001 | 3 | |
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | decrease | 7 | ||||||
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | 100uM | C2C12 myoblasts | Measured ubiquinol:cytochrome c oxidoreductase activity in broken C2C12 mitochondria after acute statin exposure at a fixed concentration for all compounds. The lactone forms of the indicated statins were included in the assay medium at their cytotoxic EC50 concentration for measurement of their effect on the catalytic capacity. | decrease | 180 | |||
| ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN | 200uM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Reduction of the CIII cytochromes c1 and b was determined spectrophotometrically in bovine heart mitochondria. | affect | p < 0.01 | 180 | |
| S,N-GLYCEROPHOSPHATE SHUTTLE | C2C12 myoblasts | affect | 180 | |||||
| SWELLING | 173.2 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | swelling assay: Absorbance at 545 nm using a fluorescence multi-well plate reader (CaCl2 (50 µM) was considered as the 100% baseline for the swelling ) | increase | EC20 | 36 |
| ROS PRODUCTION | 5 µM | 1 hour | Human | HepG2 | High-content screening assay | Increase | MEC | 306 |
| MITOCHONDRIAL DNA | depletion | 197 | ||||||
| Target | Dose | Time | Species | Model | Method | Action | Positive criterion | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex I activity | inhibitor | p < 0.01 | 3 | |
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | inhibitor | 7 | ||||||
| NADH:ubiquinone reductase | 1.6 µM | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Rotenone (2µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex I inhibition. | inhibit | EC20 | 36 |
| Succinate dehydrogenase | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex II + III activity | inhibitor | p < 0.001 | 3 | |
| Succinate dehydrogenase | ND | 60 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Oxygen consumption was monitored with 50nM MitoXpress ( an oxygen-sensitive phosphorescent dye) using a spectrofluorimeter (Tecan Infinite 200; λExcitation 380nm; λEmission 650nm). Oligomycin A (1µM) was used as 100% baseline for complex II inhibition. | Negative | EC20 | 36 |
| Quinol--cytochrome-c reductase | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex II + III activity | inhibitor | p < 0.001 | 3 | |
| Quinol--cytochrome-c reductase | 100uM | C2C12 myoblasts | Measured ubiquinol:cytochrome c oxidoreductase activity in broken C2C12 mitochondria after acute statin exposure at a fixed concentration for all compounds. The lactone forms of the indicated statins were included in the assay medium at their cytotoxic EC50 concentration for measurement of their effect on the catalytic capacity. | inhibitor | 180 | |||
| Qo site (Qp site or ubiquinol oxidation site) | 200uM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Reduction of the CIII cytochromes c1 and b was determined spectrophotometrically in bovine heart mitochondria. | inhibitor | p < 0.01 | 180 | |
| Cytochrome c oxidase | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex IV activity | inhibitor | p < 0.001 | 3 | |
| ATP synthase | 50 μM | bovine | heart mitochondria | Measurement of complex V activity | inhibitor | p < 0.001 | 3 | |
| Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | C2C12 myoblasts | inhibitor | 180 | |||||
| Reactive oxygen species | 5 µM | 1 hour | Human | HepG2 | High-content screening assay | increase | MEC | 306 |
| Cytochrome c | > 200 µM | 30 mins | mouse | liver mitochondria | Cytochrome c release was evaluated using ELISA kit ( 20 µg/ml Alamethicin was used as 100% baseline) | release | EC20 | 36 |
| Pictogram | Signal | Statements | Precautionary Statement Codes |
|---|---|---|---|
   |
Danger |
Aggregated GHS information provided by 187 companies from 23 notifications to the ECHA C&L Inventory. Each notification may be associated with multiple companies. Reported as not meeting GHS hazard criteria by 2 of 187 companies. For more detailed information, please visit ECHA C&L website Of the 22 notification(s) provided by 185 of 187 companies with hazard statement code(s): H302 (26.49%): Harmful if swallowed [Warning Acute toxicity, oral] H315 (57.3%): Causes skin irritation [Warning Skin corrosion/irritation] H317 (25.41%): May cause an allergic skin reaction [Warning Sensitization, Skin] H351 (26.49%): Suspected of causing cancer [Warning Carcinogenicity] H360 (10.81%): May damage fertility or the unborn child [Danger Reproductive toxicity] H361 (28.65%): Suspected of damaging fertility or the unborn child [Warning Reproductive toxicity] H362 (11.89%): May cause harm to breast-fed children [Reproductive toxicity, effects on or via lactation] H372 (18.92%): Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Danger Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] H373 (25.41%): Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure [Warning Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure] H411 (91.35%): Toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects [Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard] Information may vary between notifications depending on impurities, additives, and other factors. The percentage value in parenthesis indicates the notified classification ratio from companies that provide hazard codes. Only hazard codes with percentage values above 10% are shown. |
P201, P202, P260, P261, P263, P264, P270, P272, P273, P280, P281, P301+P312, P302+P352, P308+P313, P314, P321, P330, P332+P313, P333+P313, P362, P363, P391, P405, and P501; (The corresponding statement to each P-code can be found at the GHS Classification page.) |
| Organism | Test type | Route | Dose (normalized dose) | Effect | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rat | LD50 | oral | 4438mg/kg (4438mg/kg) | Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 39, Pg. 95, 1990. | |
| rat | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 705mg/kg (705mg/kg) | Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 39, Pg. 95, 1990. | |
| mouse | LD50 | oral | 3gm/kg (3000mg/kg) | Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 39, Pg. 95, 1990. | |
| dog | LD50 | oral | > 5gm/kg (5000mg/kg) | Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 39, Pg. 95, 1990. | |
| mouse | LD50 | subcutaneous | 1009mg/kg (1009mg/kg) | behavioral: muscle contraction or spasticity) | Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 39, Pg. 95, 1990. |
| women | LDLo | oral | 108mg/kg/77W- (108mg/kg) | Australian and New Zealand Journal of Medicine. Vol. 25, Pg. 745, 1995. | |
| rat | LD50 | subcutaneous | 672mg/kg (672mg/kg) | behavioral: muscle contraction or spasticity) | Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 39, Pg. 95, 1990. |
| mouse | LD50 | intraperitoneal | 798mg/kg (798mg/kg) | Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics. Vol. 39, Pg. 95, 1990. | |
| women | TDLo | oral | 2800ug/kg/7D- (2.8mg/kg) | Medical Journal of Australia. Vol. 155, Pg. 61, 1991. | |
| (+)-Simvastatin | (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-1,2,3,7,8,8a-Hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]-1-naphthalenyly-2,2-dimethyl butanoate | (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-(2-((2R,4R)-4-Hydroxy-6-oxotetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl 2,2-dimethylbu |
| (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-(2-((2R,4R)-4-Hydroxy-6-oxotetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl 2,2-dimethylbutanoate | (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-{2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxooxan-2-yl]ethyl}-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl 2,2-dimethylbutanoate | (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-{2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxotetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl}-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl 2,2-dimethylbutanoate |
| (1S,7S,8S,8aR)-8-{2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxooxan-2-yl]ethyl}-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl 2,2-dimethylbutanoate | 2,2-Dimethylbutanoic acid (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl ester | 2,2-Dimethylbutyric acid, 8-ester with (4R,6R)-6-(2-((1S,2S,6R,8S,8aR)-1,2,6,7,8,8a-hexahydro-8-hydroxy-2,6-dimethyl-1-naphthyl)ethyl)tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-2H-pyran-2-one |
| 28049-EP2269989A1 | 28049-EP2269990A1 | 28049-EP2270011A1 |
| 28049-EP2270505A1 | 28049-EP2272825A2 | 28049-EP2272841A1 |
| 28049-EP2277865A1 | 28049-EP2280001A1 | 28049-EP2280006A1 |
| 28049-EP2281813A1 | 28049-EP2284158A1 | 28049-EP2287165A2 |
| 28049-EP2287166A2 | 28049-EP2292620A2 | 28049-EP2295406A1 |
| 28049-EP2295409A1 | 28049-EP2295417A1 | 28049-EP2295422A2 |
| 28049-EP2298731A1 | 28049-EP2298742A1 | 28049-EP2298745A1 |
| 28049-EP2298769A1 | 28049-EP2298772A1 | 28049-EP2298776A1 |
| 28049-EP2298779A1 | 28049-EP2301923A1 | 28049-EP2301931A1 |
| 28049-EP2301936A1 | 28049-EP2305219A1 | 28049-EP2305648A1 |
| 28049-EP2308839A1 | 28049-EP2308878A2 | 28049-EP2314588A1 |
| 79902-63-9 | 8-[2-((2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxo(2H-3,4,5-trihydropyran-2-yl))ethyl](1S,7S,8S,3R, 8aR)-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthyl 2,2-dimethylbutanoate | 902S639 |
| 96639-EP2287163A1 | 96639-EP2305678A1 | 99548-EP2270011A1 |
| 99548-EP2298779A1 | 99548-EP2301923A1 | 99548-EP2301931A1 |
| AB00053395-07 | AB00053395-08 | AB00053395-10 |
| AB00053395_11 | AB00053395_13 | AB0069097 |
| AC-1530 | AGG2FN16EV | AKOS005111006 |
| AKOS015842733 | ARONIS24119 | AT-7048 |
| BBL024390 | BCBcMAP01_000007 | BDBM50139181 |
| BIDD:GT0769 | BPBio1_001001 | BRD-K22134346-001-05-8 |
| BRD-K22134346-001-11-6 | BRD-K22134346-001-15-7 | BRN 4768037 |
| BSPBio_000909 | BSPBio_002337 | Butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-, (1S,3R,7S,8S,*aR)-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-(2-((2R,4R)-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-1-naphthalenyl ester |
| Butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-, (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-(2-((2R,4R)-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-1-naphthalenyl ester | Butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-, (1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl]ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl ester | Butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-, 1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-(2-(tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)ethyl)-1-naphthalenyl ester, (1S-(1alpha,3alpha,7beta,8beta(2S*,4S*),8abeta))- |
| C25H38O5 | CAS-79902-63-9 | CCG-39069 |
| CCRIS 7558 | CHEBI:9150 | CHEMBL1064 |
| CPD000718785 | CS-2269 | Certified Reference Material |
| Cholestat | Coledis | Colemin |
| Corolin | D00434 | DB00641 |
| DRG-0320 | DSSTox_CID_3581 | DSSTox_GSID_23581 |
| DSSTox_RID_77090 | DTXSID0023581 | Denan |
| DivK1c_006991 | Eucor | GTPL2955 |
| HMS1570N11 | HMS1922H13 | HMS2089D12 |
| HMS2093E06 | HMS2097N11 | HMS2231N22 |
| HMS3259B12 | HMS3412P08 | HMS3676P08 |
| HMS3714N11 | HSDB 7208 | HY-17502 |
| InChI=1/C25H38O5/c1-6-25(4,5)24(28)30-21-12-15(2)11-17-8-7-16(3)20(23(17)21)10-9-19-13-18(26)14-22(27)29-19/h7-8,11,15-16,18-21,23,26H,6,9-10,12-14H2,1-5H3/t15-,16-,18+,19+,20-,21-,23-/m0/s1 | J10128 | KBio1_001935 |
| KBio2_002197 | KBio2_004765 | KBio2_007333 |
| KBio3_001557 | KBioGR_001244 | KBioSS_002197 |
| KS-1113 | Kolestevan | L 644128-000U |
| LS-46264 | Labistatin | Lipex |
| Lipinorm | Lipovas | Lodales |
| MCULE-8390617062 | MFCD00072007 | MK 0733 |
| MK 733 | MK-0733 | MK-733 |
| MLS001304029 | MLS001333077 | MLS001333078 |
| MLS002154038 | MLS006011866 | MRF-0000729 |
| Medipo | Modutrol | NC00719 |
| NCGC00016940-01 | NCGC00017324-01 | NCGC00017324-02 |
| NCGC00017324-03 | NCGC00017324-04 | NCGC00017324-05 |
| NCGC00017324-07 | NCGC00017324-08 | NCGC00017324-09 |
| NCGC00254418-01 | NSC-633782 | NSC-758706 |
| NSC633782 | NSC758706 | Nivelipol |
| Nor-Vastina | Pantok | Pharmakon1600-01504236 |
| Prestwick0_000865 | Prestwick1_000865 | Prestwick2_000865 |
| Prestwick3_000865 | Prestwick_171 | Q670131 |
| RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-HGQWONQESA- | RYMZZMVNJRMUDD-HGQWONQESA-N | Rechol |
| Rendapid | SAM002589969 | SBB080618 |
| SBI-0206773.P001 | SC-12666 | SCHEMBL2471 |
| SMR000718785 | SPBio_001881 | SPBio_002830 |
| SPECTRUM1504236 | SR-05000001894 | SR-05000001894-1 |
| SR-05000001894-2 | ST057168 | ST2407853 |
| STK801938 | Simcard | Simcor |
| Simlup | Simovil | Simvacor |
| Simvast CR | Simvastatin & Primycin | Simvastatin (JP17/USP/INN) |
| Simvastatin (Zocor) | Simvastatin [USAN:INN:BAN] | Simvastatin [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] |
| Simvastatin for peak identification, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard | Simvastatin lactone | Simvastatin(Zocor) |
| Simvastatin, 98% | Simvastatin, >=97% (HPLC), solid | Simvastatin, British Pharmacopoeia (BP) Reference Standard |
| Simvastatin, Compactin | Simvastatin, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard | Simvastatin, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard |
| Simvastatin, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard | Simvastatin, analytical standard | Simvastatin,(S) |
| Simvastatina | Simvastatina [Spanish] | Simvastatine |
| Simvastatine [French] | Simvastatinum | Simvastatinum [Latin] |
| Simvoget | Simvotin | Sinvacor |
| Sinvascor | Sivastin | SpecPlus_000895 |
| Spectrum2_001671 | Spectrum3_000669 | Spectrum4_000632 |
| Spectrum5_001428 | Spectrum_001717 | Synvinolin |
| TNP00259 | Tox21_110696 | Tox21_110696_1 |
| Tox21_300400 | UNII-AGG2FN16EV | Valemia |
| Vasotenal | Velostatin | W-3044 |
| Z1741982918 | ZINC3780893 | Zocor |
| Zocor (TN) | Zocord | Zorced |
| Zosta | [(1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-tetrahydropyran-2-yl]ethyl]-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl] 2,2-dimethylbutanoate | [(1S,3R,7S,8S,8aR)-8-[2-[(2R,4R)-4-hydroxy-6-oxooxan-2-yl]ethyl]-3,7-dimethyl-1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydronaphthalen-1-yl] 2,2-dimethylbutanoate |
| butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-,1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-(tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)-ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl ester, [1S-[1 alpha,3 alpha,7 beta,8 beta(2S*,4S*),-8a beta | inactive simvastatin | s1792 |
| simvastatin | simvastatin predrug |
| DrugBank Name | Simvastatin |
| DrugBank | DB00641 |
| CAS Number | 79902-63-9 |
| PubChem Compound | 54454 |
| KEGG Drug | D00434 |
| PubChem.Substance | 46508654 |
| ChEBI | 9150 |
| PharmGKB | PA451363 |
| ChemSpider | 49179 |
| BindingDB | 50139181.0 |
| TTD | DAP001519 |
| Wikipedia | Simvastatin |
| DPD | 1221 |